GT-IMMU
PROBIOTICS CAPSULES
30s/60s
If you’re experiencing typical H. pylori pain, heartburn, or ulcer symptoms, or you’ve tried to treat H. pylori without success, you’ll be glad to know that probiotics can be a simple and effective help. Surprisingly, various probiotic strains have emerged that can prevent H. pylori infection, significantly increase the success of H. pylori treatment, and sometimes even lead to a complete cure.
INGREDIENTS
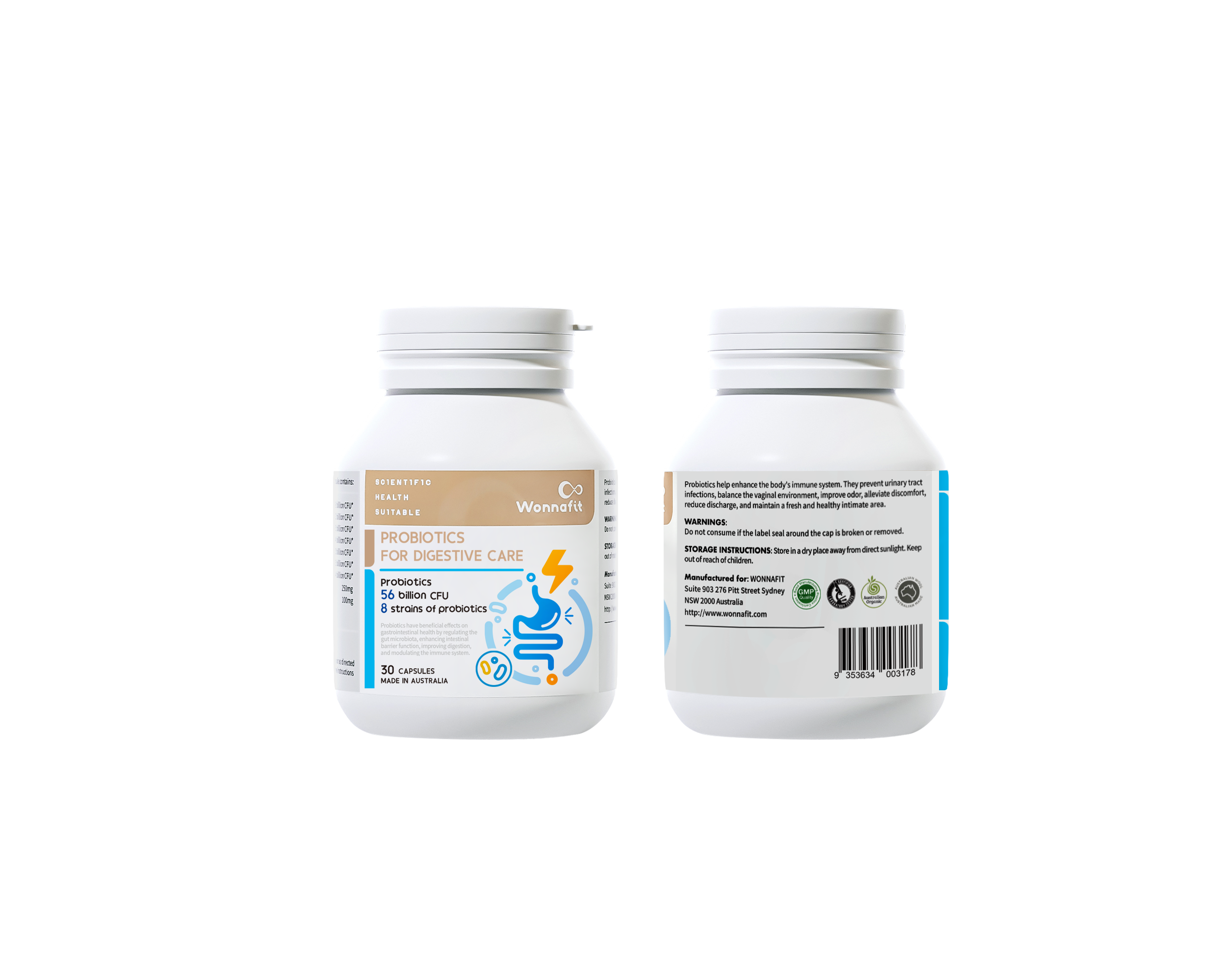
Each capsule contains:
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | 1.5 billion CFU* |
| Lactobacillus casei | 4.5 billion CFU* |
| Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. Bulgaricus | 3.5 billion CFU* |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | 3 billion CFU* |
| Bifidobacterium longum | 4 billion CFU* |
| Bifidobacterium infantis | 5 billion CFU* |
| Bifidobacterium breve | 4.5 billion CFU* |
| Streptococcus thermophilus | 30 billion CFU* |
| Total | 56 billion CFU* |
| Galacto-Oligosaccharides (Prebiotic) | 100mg |
* CFU: Colony Forming Units
HOW TO EAT:
Adults take 1 vegetarian capsule
daily with water, or as directed by
your health professional.
WARNINGS:
Do not consume if the label seal
around cap is broken or removed.
STORAGE INSTRUCTIONS:
Store in a dry place away from
direct sunlight. Use within 3 months
of opening. No refrigeration
required. Keep out of reach of
children.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding: The product can be used during pregnancy and breast-feeding.

KEY BENEFITS
- One capsule consists of a minimum of 56 Billion CFU
- Probiotics compete directly with H. pylori and help restore the gut microbial environment
- Support everyday health and wellbeing
- Maintain immune system health
- Support the intestinal microbiome
- Support healthy bowel function
- Beneficial for the treatment of diarrhea, gastroenteritis, atopic eczema, and colic.
L. = Lactobacillus
Mostly found in such as the
digestive system, urinary system,
and genital system
B. = Bifidobacterium
Bifidobacteria are one of the major
of bacteria that make up the
gastrointestinal tract
S. = Streptococcus thermophilus
Streptococcus thermophilus is a type
of probiotic (“good” bacteria) found
in the digestive tract. It produces
lactic acid in the gut.
CFU = Colony Forming Units
Unit of measurement used for
probiotics and other bacteria.
GT-IMMU FAQ
Should I take probiotics while being
treated for H. pylori?
Moreover, colonization of specific
probiotics in gastric likely
maintain the balance of the gastric
microbiota. Therefore, probiotic
supplementation is effective for
maintaining both the gastric and gut
microflora during H. pylori
infection and antibiotic therapy.
When is the best time to take
probiotics?
Taking them before breakfast may be
the preferred option, because your
digestive system has been at rest
for an extended period of time and
the probiotic has less resistance
reaching the intestines.
How many days does it take to get
rid of H. pylori?
Most people are cured after
finishing two weeks of
medicine. Some people need to take
another two weeks of medicine. It is
important to finish all of the
medicine to ensure that the bacteria
are killed.
Can probiotics heal stomach
lining?
Probiotics are a key approach to
healing leaky gut and can
repair the gut lining, reduce
inflammation, and restore the gut
microbiome. Probiotic supplements
help reduce symptoms associated with
leaky gut syndrome, including
bloating, abdominal pain, stool
changes, fatigue, and brain fog.
How long does it take for probiotics
to work?
It takes most people 2 to 3
weeks to feel significant
benefits when they start taking
probiotics. That’s because
probiotics need time to accomplish
their three key goals: increase your
good bacteria count, decrease your
bad bacteria count, and reduce
inflammation.
Why take probiotics before bed?
It’s generally recommended that you
take probiotics before bedtime.
This gives the beneficial
bacteria time to colonize in your
gut overnight. When you sleep, your
body’s digestive system slows down.
What are the benefits of GOS
prebiotics?
Giving a formula that contains
prebiotics, including GOS, to
infants with colic might help reduce
crying. Inability to properly digest
the sugar lactose (lactose
intolerance). Taking GOS by mouth
might improve symptoms like stomach
pain, cramps, and bloating in people
who are lactose intolerant.
Is Galactooligosaccharides good for
you?
Galacto-oligosaccharides pass
undigested into the colon where they
increase bowel mass and promote
growth of certain bacteria that are
thought to be beneficial.
REFERENCES:
1. de Brito BB, da Silva FA,
Soares AS, et al.: Pathogenesis
and clinical management of
Helicobacter pylorigastric
infection. World J Gastroenterol.
2019, 25:5578-89.
10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5578
2. Goderska K, Agudo Pena S,
Alarcon T: Helicobacter pylori
treatment: antibiotics or
probiotics . Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 2018, 102:1-7.
10.1007/s00253-017-8535-7
3. Chen L, Xu W, Lee A, et al.:
The impact of Helicobacter pylori
infection, eradication therapy and
probiotic supplementation on gut
microenvironment homeostasis: an
open-label, randomized clinical
trial.EBioMedicine. 2018,
35:87-96.
10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.08.028
4. Eaton KA, Morgan DR, Krakowka
S: Motility as a factor in the
colonisation of gnotobiotic
piglets by Helicobacter pylori. J
Med Microbiol. 1992, 37:123-7.
10.1099/00222615-37-2-123
5. Clyne M, Ocroinin T, Suerbaum
S, Josenhans C, Drumm B: Adherence
of isogenic flagellum-negative
mutants of Helicobacter pylori and
Helicobacter mustelae to human and
ferret gastric epithelial cells.
Infect Immun. 2000, 68:4335-9.
10.1128/IAI.68.7.4335-4339.2000
6. Aizawa SI, Harwood CS, Kadner
RJ: Signaling components in
bacterial locomotion and sensory
reception . J Bacteriol. 2000,
182:1459-71.
10.1128/JB.182.6.1459-1471.2000
7. Food and Agriculture
Organization of the United Nations
(FAO). In: Encyclopedia of Global
Health . (2008).Accessed: June 1,
2022:
http://dx.doi.org/10.4135/9781412963855.n464.
8. Lionetti E, Indrio F, Pavone
L, Borrelli G, Cavallo L,
Francavilla R: Role of probiotics
in pediatric patients with
Helicobacter pylori infection: a
comprehensive review of the
literature. Helicobacter. 2010,
15:79-87.10.1111/j.1523-5378.2009.00743.x
9. Lesbros-Pantoflickova D,
Corthésy-Theulaz I, Blum AL:
Helicobacter pylori and probiotics
. J Nutr. 2007,137:812S-8S.
10.1093/jn/137.3.812S
10. Batdorj B, Trinetta V,
Dalgalarrondo M, et al.:
Isolation, taxonomic
identification and hydrogen
peroxide production by
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp.
lactis T31, isolated from
Mongolian yoghurt: inhibitory
activity on food-borne pathogens.
J Appl Microbiol. 2007,
103:584-93.
10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03279.x
11. Felley C, Michetti P:
Probiotics and Helicobacter
pylori. . Best Practice Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 2003, 17:785-91.
10.1016/s1521-6918(03)00070-2
12. Guruge JL, Falk PG, Lorenz
RG, et al.: Epithelial attachment
alters the outcome of Helicobacter
pylori infection. Proc Natl Acad
Sci U S A. 1998, 95:3925-30.
10.1073/pnas.95.7.3925
13. Çekin AH, Şahintürk Y, Akbay
Harmandar F, Uyar S, Yolcular BO,
Çekin Y: Use of probiotics as an
adjuvant to sequential H. pylori
eradication therapy: impact on
eradication rates, treatment
resistance, treatment related side
effects, and patient compliance.
Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017,
28:3-11.
10.5152/tjg.2016.0278
14. Oh B, Kim BS, Kim JW, et al.:
The effect of probiotics on gut
microbiota during the Helicobacter
pylori eradication: randomized
controlled trial. Helicobacter.
2016, 21:165-74.
10.1111/hel.12270
15. Losurdo G, Cubisino R, Barone
M, Principi M, Leandro G, Ierardi
E, Di Leo A: Probiotic monotherapy
and Helicobacter pylori
eradication: a systematic review
with pooled-data analysis. World J
Gastroenterol. 2018,24:139-49.
10.3748/wjg.v24.i1.139
16. Dore MP, Cuccu M, Pes GM,
Manca A, Graham DY: Lactobacillus
reuteri in the treatment of
Helicobacter pylori infection.
Intern Emerg Med. 2014, 9:649-54.
10.1007/s11739-013-1013-z
17. Yuan Z, Xiao S, Li S, et al.:
The impact of Helicobacter pylori
infection, eradication therapy,
and probiotics intervention on
gastric microbiota in young
adults. Helicobacter. 2021,
26:e12848. 10.1111/hel.12848
18. Viazis N, Argyriou K,
Kotzampassi K, et al.: A
four-probiotics regimen combined
with a standard Helicobacter
pylori-eradication treatment
reduces side effects and increases
eradication rates. Nutrients.2022,
14:632. 10.3390/nu14030632
19. Shi X, Zhang J, Mo L, Shi J,
Qin M, Huang X: Efficacy and
safety of probiotics in
eradicating Helicobacter pylori: a
network meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 2019, 98:e15180.
10.1097/MD.0000000000015180
20. Márquez CM, Álvarez PF,
Delgado TV, Laria LC, Arias FA,
Álvarez ÁC, Rodríguez BJG:
Randomized, double blind,
placebo-controlled clinical trial
on the usefulness of probiotic
Lactobacillus reuteri in bismuth
containing quadruple eradication
therapy for infection with
Helicobacter pylori. Rev Esp
Enferm Dig. 2022,114:89-95.
10.17235/reed.2021.7931/2021
21. Sniffen JC, McFarland LV,
Evans CT, Goldstein EJ: Choosing
an appropriate probiotic product
for your patient: an
evidence-based practical guide.
PLoS One. 2018, 13:e0209205.
10.1371/journal.pone.0209205
22. Hempel S, Newberry SJ, Maher
AR, et al.: Probiotics for the
prevention and treatment of
antibiotic associated diarrhea: a
systematic review and
meta-analysis. JAMA. 2012,
307:1959
69.10.1001/jama.2012.3507
